THE TAIWAN CLEARING HOUSE
IndexIntroductionBusinessBusiness
The business of the TCH (Taiwan Clearing House) is primarily associated with the following categories:
1.Check Clearing and Dishonored Check Clearing
2.Filing Information on Dishonored Checks, The Announcement of Lost Checks, Application of Cancellation of Payment Orders
3.Filing The Information of Opening Checking Accounts
4.Administrative Management of Check Credit Information
5.The Enquiry Service for Check Credit Information
6.ACH(Automated Clearing House) Operation
7.Bill for Collection for Financial Institutions
8.FCS(Financial Collection System) Operation
9.Electronic Direct Debit Authorization (eDDA)
10.Enhanced Automated Clearing House (eACH)
11.Enhanced Financial Collection Service (eFCS)
The details of the business are described as follows.
1. Check and Dishonored Check Clearing
(1) Check Clearing
Check clearing operations in the Taipei area has improved from manual to computer processing by Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) System since January 4, 1985. This technology can instantly read the information printed by the magnetic ink on the bottom of the checks for automated check processing and clearing. In succession, Taichung City Branch, Kaohsiung City Branch adopted MICR system for check clearing in 1994 and 1997 respectively.
After reorganization, the TCH has plan to arrange the head office in Taipei, Taichung City Branch and Kaohsiung City Branch as north, middle and south regional computerized check clearing centers, and has continuously merged the check clearing business of the neighboring branches into these 3 check clearing centers since October, 2003.
North Clearing Center (Taipei Head Office): clearing checks of head office and the 2 branches in Taoyuan City, Hsinchu City.
Middle Clearing Center (Taichung City Branch): clearing checks of the 2 branches in Taichung City and Chiayi City.
South Clearing Center (Kaohsing City Branch): clearing checks of the 2 branches in Kaohsiung City and Tainan City.
(Check Clearing Flow Chart)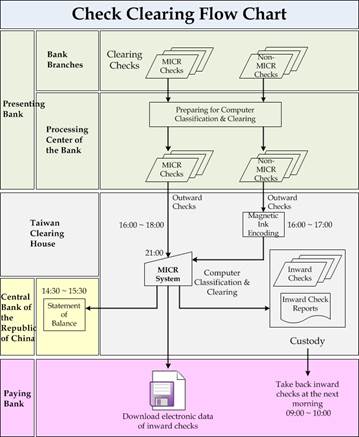
Until now, only the branch offices in Hualien County, Taitung County, and Penghu County still use manual processing.
The staff of each clearing unit in these areas delivers the presenting checks to the local branch clearing office and fills up a check clearing form for check clearing. Each drawer bank respectively receive its checks through the branch office with the submission form. The local branch office then summarizes the differential amount of each clearing unit and the statement of balance goes to the local branch of BOT for final settlement.
(2) Dishonored Check Clearing
The exchange of dishonored checks was originally processed manually in the early days. Each bank sent their staff to the local clearing house for clearing dishonored checks following the specific timetable. In order to increase efficiency and computerize the process of dishonored check clearing, the computerized dishonored check clearing and settlement system was introduced by the Taipei Head Office on July 1, 1999. The data of the dishonored checks, which used to be processed manually, begun to be transferred to the clearing center through networks and balanced electronically afterwards. The physical dishonored checks were left in the safe box which was categorized by the original presenting banks (payee bank) and installed in the local clearinghouse. Each bank may take back the physical dishonored check from its own safe box, respectively.
On April 17, 2002, Taichung and Kaohsiung city branches tailed and implemented the same system due to admirable performance of the improved system. On August 1, 2002, Taoyuan, Hsinchu and Tainan Branches subsequently put this system into practice. All branches in the western Taiwan have integrated into this system since September 1, 2003. In the eastern Taiwan, the branch office in Ilan County was integrated into the same system on July 18, 2006. Branch offices only in Hualien County, Taitung County, and Penghu County still remain manual processing.
(Dishonored Check Clearing Flow)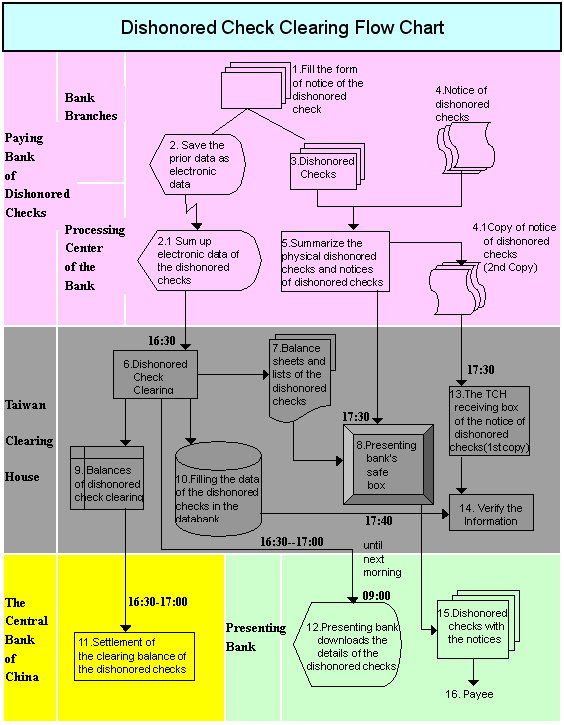
(3) Settlement of the Balance of Checks and Dishonored Checks
In order to facilitate the participating financial institutions to centralized adjust and manage their funds, the clearing balance of the Taichung Branch and the Kaohsiung Branch have been electronically transmitted to and merged into the Taipei head office since July 1,2002. The net clearing balances of the 3 clearing centers will be subsequently sent to the CBC (Central Bank of the Republic of China) for final settlement. Now, for all computer processing branch offices and the head office, the net balance is centralized sent to the CBC for settlement. As to the manual processing areas, the net balance will go to the local branch of BOT for settlement.
2. Filing Information on Dishonored Checks, the Announcement of Lost Checks, Application of Cancellation of Payment Orders
The CBC in Taiwan promulgated “The Project of Filing the Information and Computerized Enquiry on Dishonored Check Accounts in Taiwan Area” in 1985 in order to strengthen the check credit reference system in Taiwan. The TCH was responsible for collecting information related to dishonored checks (including non-sufficient funds, issued with incorrect signatures or stamps, cancellation of payment order before mandatory presentment day, promissory notes issued payable through a bank without the paying bank’s prior approval, and dishonored accounts nationwide, etc.). A databank, “The Database of Dishonored Accounts and Dishonored Checks Nationwide” was established in the information center of the TCH. The general public may obtain the information online. This check credit information enquiry service has been offered since November 6, 1987. In order to concrete the content information, the TCH has invited a new check credit management system, since July 1, 2001, to file the announcement of lost checks, and application of cancellation of payment orders as additional information for public enquiry.
3. Filing the Information of Opening Checking Accounts
In order to protect the rights of check holders and build a sound check circulation environment, the TCH has planed to file the information on opening checking accounts (including NT account and OBU foreign currency account) in Taiwan since November, 1995, so that the public in general may use the business uniform code of the paying institution with the checking account number to query the data of related accounts information of any check issuer. This enquiry service started in September 1998.
4. Administrative Management of Check Credit Information
Administrative management of the check credit information may be classified into the following categories:
(1) Collect and update the information of dishonored checks, checking accounts nationwide, the announcement of lost checks, application of cancellation of payment orders, etc.
(2) Screen and file the application for remark of reimbursement of the dishonored check records.
(3) Circulating the dishonored accounts.
Management of the Check Credit Information Flow Chart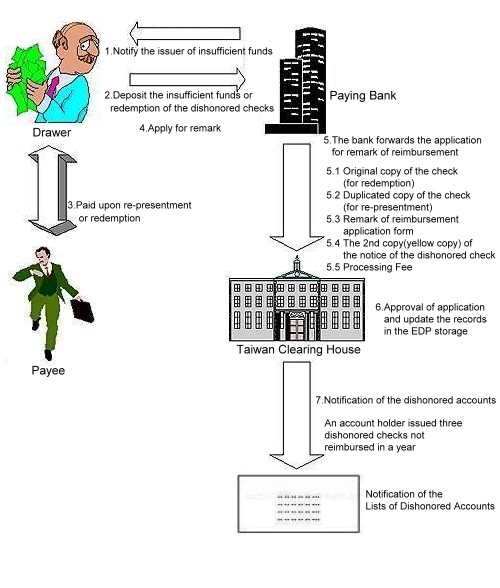
5. The Enquiry Service for Check Credit Information
(1) Categories of Enquiry
1st Category
Providing information on the subject of enquiry including total number of dishonored checks, amount and other related check credit information within the past 3 years.
2nd Category
Providing information on the subjects of inquiry including total number of dishonored checks, amount, the detail lists of the dishonored checks, and other check credit related information in the past 3 years.
3rd Category
Providing information on the subjects of inquiry including the volumes of dishonored checks due to non-sufficient funds that occurred within the past one year and whether it is a dishonored account.
(The following two categories can be inquired by financial institutions only.)
Category A
Providing information on the subjects of inquiry including total number of dishonored checks, amount, the detail lists of the dishonored checks, and check credit related information in the past 3 years if each check amount is not less than the amount of 500,000 NTD.
Category B
Providing the latest 3 records on the subjects of the detail lists of the dishonored checks, and check credit related information in the past 3 years, if each check amount is not less than the amount of 500,000 NTD.
Dishonored checks, which were reimbursed and remarked, or dismissal in advance of a dishonored account over 6 months in the database, the record will be excluded in the 1st ,2nd and 3rd category enquiry service. Dishonored checks, which were reimbursed and remarked over 6 months in the database, the record will be excluded in the category A and B enquiry service.
(2) How to Make An Enquiry
◆ Written enquiry.
Any individual may inquire the information from the TCH, head offices and its branch offices, or any other online banks. The TCH offer this service from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m.
◆ Connect to the Internet.
The website URL is http://www.twnch.org.tw
◆ By telephone.
Please dial 02-23910379.
◆ Through electronic media.
Results of large volume enquiry are available by network transmission or Email delivery.
6. ACH (Automated Clearing House) Operation
With the development of information and telecommunication technology, payment instruments have moved into an era of diversification. To enhance payment system efficiency nationwide, the TCH has formally introduced the Automated Clearing House (ACH) transaction service to the public since June 7, 2002.
The ACH network is based on electronic batch processing, by this mechanism which companies or organizations (originators) may authorize financial institutions (Originating Financial Deposit Institution, OFDI) to collect or pay funds for them. In other words, the former (to collect) is a direct debit, and the latter (to pay) is a direct credit. The data of both direct debit and direct credit will be transferred to the TCH through network for transaction and later balance. And, the balance will be sent to the CBC for settlement.
◆ Direct Debit :The direct debit service help originators (e.g. payees) collect utility fees, telephone bills, gas bills, cable access charges, credit card bills and or school tuition, etc from the payers (message receivers). (ACH debits)
◆ Direct Credit :The direct credit service help originators (e.g. payers) pay wages or salaries , stock dividends, insurance premiums, pension and annuities for elders, etc. (ACH credits)
The main features of the TCH’s ACH operations are:
(1) The TCH is an experienced institution in the field of inter-bank clearing with clearly defined business rules and thorough operational regulations.
(2) The TCH settle the balance on a net basis, which helps the banks lower the business operating costs and utilize their funds more effectively.
(3) The TCH clearing network is widely spread over Taiwan.
(4) The TCH clearing network is secure and efficient so that both originators and receivers are satisfied with and trust our services.
7. Bill for Collection for Financial Institutions
In order to enhance the payment efficiency and ensure financial institutions’ well operations of bill for collection (B/C) covering the remote districts of Taiwan. Since January, 2007, the participating clearing units of the TCH may authorize the TCH to collect and deliver the physical checks to the areas of non-participating for clearing or manual processing for clearing, (that is, Hualien County, Taitung County, Penghu County).
The physical checks, which is successfully cashed, will be direct transacted through the network of the ACH system and transfer the amount to the payee bank; however; if unsuccessful, the physical checks will be deliver to the payee bank from the dwawer bank though the TCH’s delivery.
8. FCS (Financial Collection System) Operation
The FCS (Financial Collection System) refers to the payment system that facilitates the payers to pay directly in front of the counters of financial institutions with cash and the debit notes, or by electronic payment systems such as Internet banking or telephone banking. In order to promote the efficiency, since October 4, 2010, the TCH has offered this platform for financial institutions. Offering this platform can not only reduce the setup and following maintaining costs of each participating financial institution, but also simplify the tedious procedures for publicly owned corporations and enterprises without the needs of signing contract with every delegated financial institution. That is, they may simplify the process to authorize one originator bank to complete the operations such as fund transferring, files exchanging and reporting.
9. Electronic Direct Debit Authorization (eDDA)
To enhance the efficiency of Direct Debit Authorizations (DDA), the TCH launched the Electronic Direct Debit Authorization (eDDA) service on April 30, 2015, aimed at streamlining the process of Direct Debit Authorizations (DDA). eDDA enables individuals to authorize bank account linkages and complete identity verification online—without the need for paper forms or physical visits to the bank.
Through both card-based (e.g., ATM card, Citizen Digital Certificates, ATMs, or kiosks) and cardless methods (e.g., internet/mobile banking, Bank Account Authentication, and Mobile ID), users can conveniently and securely complete authorization procedures.
This service not only simplifies the application process but also offers real-time authorization results, enhancing overall efficiency and user experience in financial transactions.
10. Enhanced Automated Clearing House (eACH)
To meet the demand from businesses for faster collections and payments processing, the TCH launched the Enhanced Automated Clearing House (eACH) service on June 29, 2015.
eACH facilitates seamless credit transfers and direct debits for a wide spectrum of industries, including Customer Ledgers of Securities Firms' Settlement Accounts, insurance premium, insurance benefits, insurance loan disbursements, mortgage, business transactions and merchant fund transfers.
With 24/7 availability, eACH enables real-time debit and credit processing, offering businesses and individuals a convenient and efficient solution for credit transfers and direct debits.
11. Enhanced Financial Collection Service (eFCS)
To facilitate convenient bill payments for the public, the TCH launched the Enhanced Financial Collection Service (eFCS) on November 13, 2017. The integrated platform allows users to instantly retrieve billing information or scan bill barcodes via familiar mobile payment apps, financial institutions, or electronic payment channels.
Billing entities are not required to modify their existing billing or reconciliation systems, enabling rapid adoption of mobile payment services. Through a single point of contact with the Institute or clearing bank, it streamlines processes, accelerates fund settlement, and enhances cash flow flexibility.
eFCS currently supports a wide range of payments, including utilities (water, electricity, gas, telecom), vehicle fuel usage fees, traffic fines, local taxes (excluding offshore islands), and certain tuition and administrative fees across various municipalities.